Spark 笔记
Why not hadoop
Why data sharing in Hadoop is slow
Both Iterative and Interactive applications require faster data sharing across parallel jobs. Data sharing is slow in MapReduce due to replication, serialization, and disk IO. Regarding storage system, most of the Hadoop applications, they spend more than 90% of the time doing HDFS read-write operations.
Motivation of Spark
- Iterative jobs: Many common machine learning algorithms apply a function repeatedly to the same dataset to optimize a parameter (e.g., through gradient descent). While each iteration can be expressed as a MapReduce/Dryad job, each job must reload the data from disk, incurring a significant performance penalty.
- Interactive analytics: Hadoop is often used to run ad-hoc exploratory queries on large datasets. Ideally, a user would be able to load a dataset of interest into memory across a number of machines and query it repeatedly. However, with Hadoop, each query incurs significant latency (tens of seconds) because it runs as a separate MapReduce job and reads data from disk
Features of Spark
Apache Spark has following features.
-
Speed − Spark helps to run an application in Hadoop cluster, up to 100 times faster in memory, and 10 times faster when running on disk. This is possible by reducing number of read/write operations to disk. It stores the intermediate processing data in memory.
-
Supports multiple languages − Spark provides built-in APIs in Java, Scala, or Python. Therefore, you can write applications in different languages. Spark comes up with 80 high-level operators for interactive querying.
-
Advanced Analytics − Spark not only supports ‘Map’ and ‘reduce’. It also supports SQL queries, Streaming data, Machine learning (ML), and Graph algorithms.
RDD
A resilient distributed dataset (RDD) is a Distributed Collection of Key-Value Pairs. RDD is a read-only collection of objects partitioned across a set of machines that can be rebuilt if a partition is lost. The elements of an RDD need not exist in physical storage; instead, a handle to an RDD contains enough information to compute the RDD starting from data in reliable storage. This means that RDDs can always be reconstructed if nodes fail.
Data sharing using Spark RDD
Recognizing this problem, researchers developed a specialized framework called Apache Spark. The key idea of spark is Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD); it supports in-memory processing computation. This means, it stores the state of memory as an object across the jobs and the object is sharable between those jobs. Data sharing in memory is 10 to 100 times faster than network and Disk.
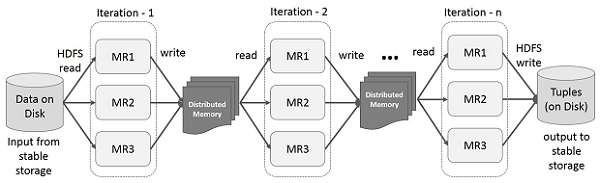
If the Distributed memory (RAM) is not sufficient to store intermediate results (State of the JOB), then it will store those results on the disk.
Reference
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/apache_spark/apache_spark_introduction.htm